Research
The overarching goal of our is to advance the mechanistic understanding of human cancer genome regulation and dissect how transcription factors alter cancer genome folding. The lab expertise in chromatin, cancer, and computational biology allows us to deploy multidisciplinary approaches to rigorously define the cause-and-effect relationship between transcriptional regulators, chromatin organization, and gene expression in cancer. Current projects in the lab focuses on lymphoma and breast cancer and explore: i) how epigenetic control of gene expression is disrupted, ii) how transcriptional dependencies can develop, and iii) how heterogeneity and plasticity of transcriptional dependencies enable drug resistance in these cancers.
RESEARCH AREAS
Deciphering Mechanisms of Genome Mis-folding In Cancer
Our lab deploys data-rich experimental techniques to elucidate the role of genome mis-folding in controlling oncogenic gene expression programs. Specifically, we are interested in moving beyond the status quo to understand how oncogenic subversion of lineage-determining transcription factors set topology of cancer genome. To tackle this question, we combine genomics and super-resolution imaging and focus on investigating molecular mechanisms of genome mis-folding in breast and blood cancers. These mechanistic studies aim to identify precise epigenetic vulnerabilities of cancer cells and guide treatments disrupting cancer cells’ transcriptional addiction.
Representative Publication
Oncogenic Notch Promotes Long-Range Regulatory Interactions Within Hyperconnected 3D Cliques.
Petrovic J*, Zhou Y*, Fasolino M, Goldman N, Schwartz GW, Mumbach MR, Nguyen SC, Rome KS, Sela Y, Zapataro Z, Blacklow SC, Kruhlak MJ, Shi J, Aster JC, Joyce EF, Little SC, Vahedi G, Pear WS, Faryabi RB Molecular Cell. 2019;73(6):1174-90 e12
PubMed PMID: 30745086;
PMCID: PMC6485942
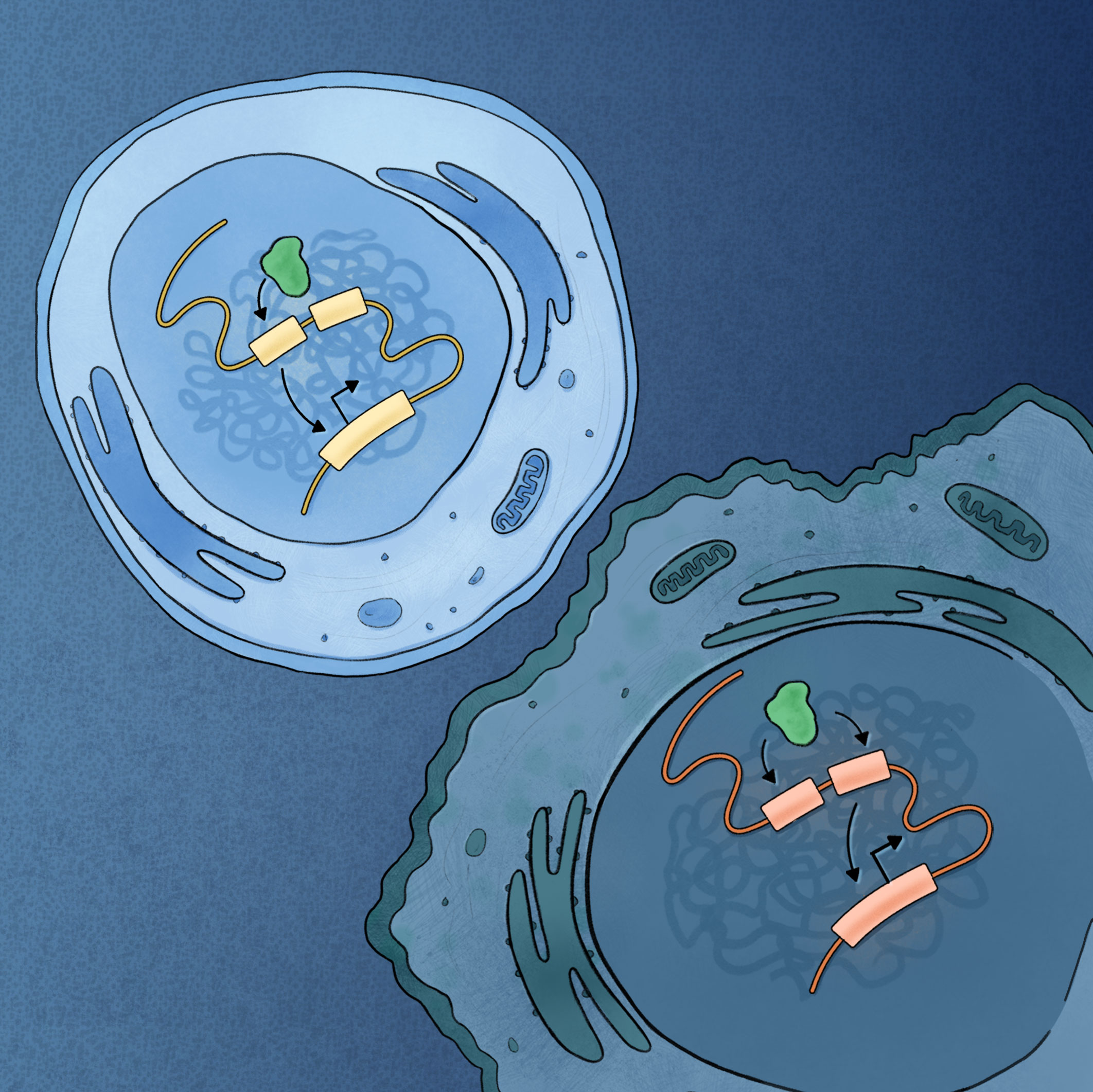
Determining Epigenetic Mechanisms Of Resistance To Targeted Therapies
Targeting oncogenic drivers of cancers commonly leads to drug resistance. Mechanisms of acquiring resistance to oncology drugs mostly remain unknown, partly due to the limitations of population-based assays in elucidating heterogeneity of drug-naive and complexity of drug-induced tumor evolution. Using single-cell genomics and imaging, we study how heterogeneity and plasticity of transcriptional dependencies confer resistance to targeted therapeutics such as Notch inhibitors.
Representative Publication
EBF1 nuclear repositioning instructs chromatin refolding to promote therapy resistance in T leukemic cells
Zhou Y, Petrovic J, Zhao J, Zhang W, Bigdeli A, Zhang Z, Berger SL, Pear WS, Faryabi RB Molecular Cell, 2022
PubMed PMID: 35182476;
PMCID:
Innovating Computational Methods To Enable Cancer Discovery
Our lab innovates statistical and machine learning approaches to accelerate discovery of novel therapeutics and biomarkers by elucidating complexity and heterogeneity of tumors. Recently, we have developed a computational ecosystem for mapping molecular and spatial heterogeneity in tumors. As part of the Center for Personalized Diagnostics, we also mine cancer patient genotypic/phenotypic data to improve patient health. patient health.
Representative Publication
TooManyCells Identifies And Visualizes Relationships Of Single-cell Clades.
Schwartz GW, Zhou Y, Petrovic J, Fasolino M, Xu L, Shaffer SM, Pear WS, Vahedi G, Faryabi RB Nature Methods, 2020; 17: 405-413
PubMed PMID: 32123397;
PMCID: PMC7439807
